Introduction to ABS Injection Moulding
ABS injection moulding is a highly versatile and widely used manufacturing process that plays a crucial role in the production of various plastic components across multiple industries. It involves injecting melted ABS resin into a mould cavity under high pressure to create intricate and precise shapes. The significance of ABS injection moulding lies in its ability to produce parts with excellent dimensional accuracy, complex geometries, and high surface finishes, making it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking cost-effective and efficient production methods.
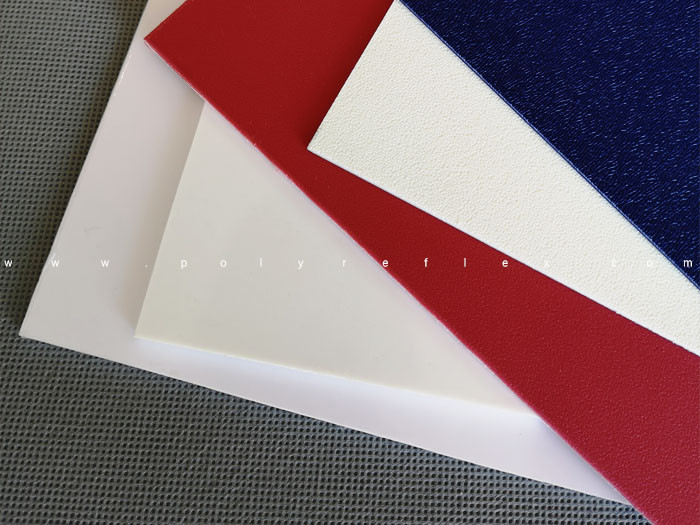
ABS, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a thermoplastic polymer known for its exceptional mechanical properties and versatility. It is composed of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, which collectively contribute to its unique characteristics. ABS offers a remarkable balance of strength, impact resistance, and heat resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Its ability to be easily colored, textured, and finished further enhances its appeal in various industries.
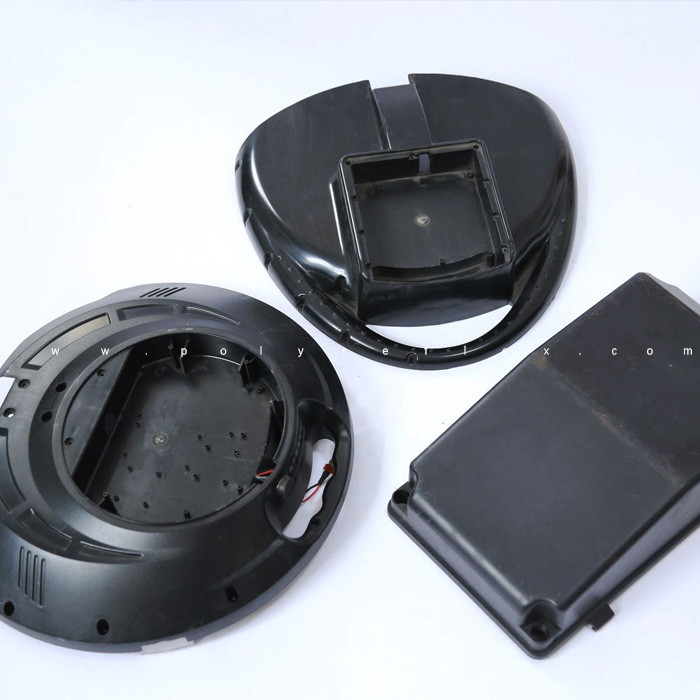
In ABS injection moulding, the ABS resin is heated until it reaches a molten state and is then injected into a mould cavity at high pressure. Once inside the mould, the molten resin takes the shape of the cavity and cools rapidly to solidify into the desired part. This process allows for the efficient and precise production of complex shapes and intricate details, making ABS injection moulding a preferred choice for manufacturing components such as automotive parts, consumer goods, electronic enclosures, and medical devices.
The Process of ABS Injection Moulding
ABS injection moulding is a precise and intricate process that involves several sequential steps to produce high-quality plastic parts. Understanding each stage of the process is crucial for achieving optimal results in manufacturing.
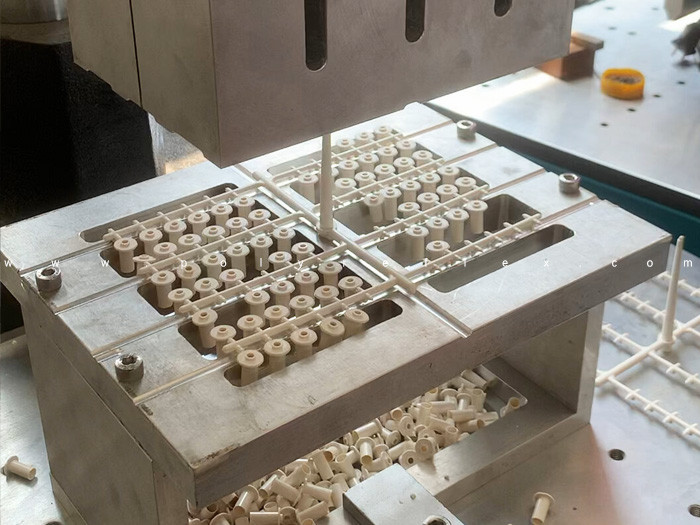
1. Melting: The first step in ABS injection moulding is melting the ABS resin pellets. This is typically done in a heated barrel of an injection moulding machine. The pellets are fed into the barrel, where they are subjected to high temperatures, causing them to melt into a molten state. The temperature of the barrel is carefully controlled to ensure proper melting without degradation of the material.
2. Injection: Once the ABS resin is melted, it is injected into a mould cavity under high pressure. The injection process involves the use of a reciprocating screw or plunger mechanism to force the molten resin into the mould. The mould cavity is precisely designed to shape the molten resin into the desired geometry of the final part. The pressure applied during injection is critical for filling the mould cavity completely and minimizing defects such as voids or sink marks.
3. Cooling: After the molten resin is injected into the mould cavity, it begins to cool and solidify. Cooling is typically achieved by circulating coolant through channels in the mould or by using air or water jets to rapidly cool the mould surface. Proper cooling is essential for achieving uniform solidification of the part and preventing warping or distortion. The cooling time required depends on factors such as the thickness of the part, the material used, and the design of the mould.
4. Ejection: Once the part has sufficiently cooled and solidified, the mould opens, and the finished part is ejected from the mould cavity. Ejection can be facilitated by mechanical pins, ejector plates, or hydraulic actuators. Care must be taken during ejection to avoid damaging the part or the mould. Proper mould design and ejection mechanisms are essential for ensuring smooth and efficient part removal.
Advantages of ABS Injection Moulding
ABS injection moulding offers a multitude of advantages that make it a preferred choice for manufacturers across various industries. Understanding these benefits is essential for appreciating the versatility and effectiveness of ABS in injection moulding processes.
1. Strength and Impact Resistance
ABS exhibits exceptional strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for producing durable and robust plastic parts. Its ability to withstand external forces and impacts ensures that the final components maintain structural integrity even under demanding conditions. This makes ABS ideal for applications requiring toughness and reliability, such as automotive components, electronic enclosures, and consumer goods.
3. Ease of Coloring, Texturing, and Finishing
ABS resin can be easily colored using a wide range of pigments and dyes, allowing for vibrant and customized finishes on injection-moulded parts. Additionally, ABS readily accepts surface textures and patterns, providing opportunities for enhancing aesthetic appeal and functionality. Whether it's a smooth, glossy finish or a textured, matte surface, ABS offers versatility in achieving desired visual and tactile effects. Furthermore, ABS parts can be readily post-processed with techniques such as painting, plating, or printing to further enhance their appearance and functionality.
4. Chemical Resistance and Durability
ABS exhibits excellent resistance to chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it suitable for applications exposed to harsh environments or corrosive substances. This chemical resistance enhances the durability and longevity of ABS parts, ensuring they maintain their performance and appearance over time. This makes ABS an ideal choice for components used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, where exposure to various chemicals is common.
In conclusion, ABS injection moulding offers a multitude of advantages that make it a versatile and efficient manufacturing process for producing high-quality plastic components. From its strength and impact resistance to its versatility in design and finishing options, ABS provides manufacturers with the flexibility and reliability needed to meet the diverse requirements of modern industries. By leveraging the benefits of ABS injection moulding, manufacturers can achieve superior results and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Applications of ABS Injection Moulding
ABS sheets offer numerous advantages when used in vacuum forming processes, making them a preferred choice for a wide range of applications. Let's explore these advantages in detail:
1. Automotive Parts: ABS is extensively used in the automotive industry for manufacturing various interior and exterior components. These include dashboard panels, door handles, trim pieces, and interior trim. ABS's strength, impact resistance, and ability to be easily colored make it an ideal choice for automotive parts requiring both aesthetic appeal and durability.
2. Electronics Housings: Electronic devices often require durable and protective housings to encase delicate components and circuitry. ABS is well-suited for this purpose due to its excellent electrical insulation properties and impact resistance. It is commonly used to manufacture housings for consumer electronics such as computer peripherals, televisions, audio equipment, and home appliances.
3. Consumer Goods: ABS injection moulding is prevalent in the production of various consumer goods due to its versatility and aesthetic appeal. Examples include household appliances, toys, sporting goods, and luggage. ABS's ability to be easily molded into different shapes, colors, and textures allows for the creation of attractive and functional consumer products that meet market demands.
4. Medical Devices: In the medical industry, ABS is utilized for manufacturing a wide range of devices and equipment. This includes medical instrument housings, equipment enclosures, and disposable medical devices. ABS's biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and ease of sterilization make it suitable for applications requiring stringent regulatory compliance and durability in medical settings.
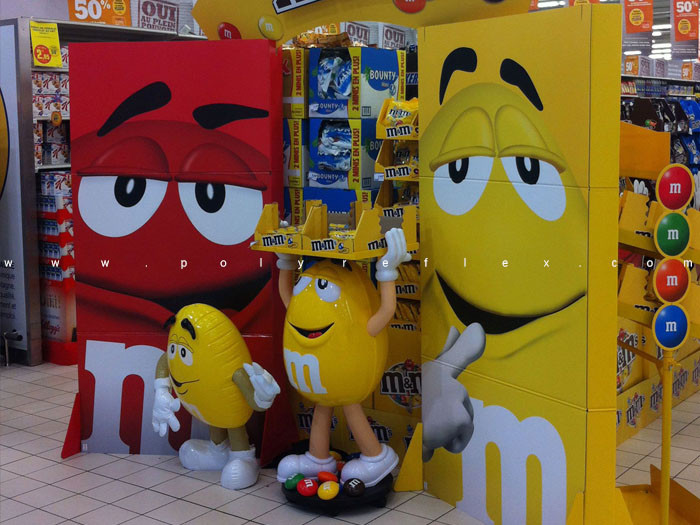
5. Point-of-Purchase Displays: ABS injection moulding is commonly employed in the production of point-of-purchase (POP) displays used in retail environments. These displays showcase products and promotional materials, requiring durability, aesthetics, and customization options. ABS's ability to be easily molded into various shapes and sizes, along with its ability to accept different surface finishes, makes it an ideal material for POP displays.
6. Furniture Components: ABS injection moulding is utilized in the furniture industry for manufacturing various components such as chair arms, legs, and trim pieces. ABS's strength, impact resistance, and ease of finishing allow for the production of durable and visually appealing furniture components that withstand everyday use and environmental conditions.
7. Building and Construction: ABS is also used in the building and construction industry for applications such as pipe fittings, door and window profiles, and decorative trim. Its weather resistance, dimensional stability, and ease of processing make it suitable for both interior and exterior building components that require durability and aesthetics.
In summary, ABS injection moulding finds extensive applications across industries such as automotive, electronics, consumer goods, medical devices, retail, furniture, and building construction. Its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking high-quality plastic components that meet diverse market demands.
Considerations During ABS Injection Molding
ABS injection moulding presents considerations and challenges that manufacturers must address for successful production and minimal defects:
1. Shrinkage: ABS tends to shrink as it cools, leading to dimensional inaccuracies and warping. Control parameters like melt temperature and cooling rate to minimize shrinkage.
2. Warping: Uneven cooling can cause warping, particularly in large or thick-walled parts. Employ techniques such as uniform mould cooling or part design modifications to mitigate warping.
3. Design Complexity: Complex geometries and thin walls can pose challenges during mould filling and ejection. Consider draft angles and wall thickness to ensure smooth production.
4. Material Selection: Choose the appropriate ABS resin grade based on desired properties and performance. Additives can enhance characteristics like stiffness or flame retardancy.
5. Tooling and Mould Design: Quality mould design is crucial for defect-free parts. Poor venting or gate placement can lead to defects like air traps or sink marks. Invest in high-quality tooling and maintenance.
6. Processing Parameters: Optimize parameters such as injection speed and pressure for desired part quality. Fine-tune parameters to prevent issues like flashing or incomplete filling.
In conclusion, addressing these considerations ensures successful ABS injection moulding. By optimizing processes and addressing challenges, manufacturers can produce high-quality ABS parts that meet performance standards.
In conclusion, ABS injection moulding stands out as a versatile and indispensable manufacturing process that offers numerous advantages across a wide range of industries. ABS injection moulding enables the production of high-quality plastic parts with exceptional strength, impact resistance, and dimensional accuracy. Its versatility allows for the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs, while its ease of coloring, texturing, and finishing provides endless customization options. Moreover, ABS's durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking reliable and efficient solutions for their plastic component needs.
From automotive parts and electronics housings to consumer goods and medical devices, ABS injection moulding finds widespread use in various industries, showcasing its adaptability and effectiveness in meeting diverse market demands. In essence, ABS injection moulding embodies innovation, reliability, and efficiency in modern manufacturing processes. Its importance and versatility make it a cornerstone of plastic component production, driving advancements and meeting the evolving needs of industries worldwide. By leveraging the benefits of ABS injection moulding, manufacturers can achieve superior results, streamline production, and gain a competitive edge in today's dynamic marketplace.