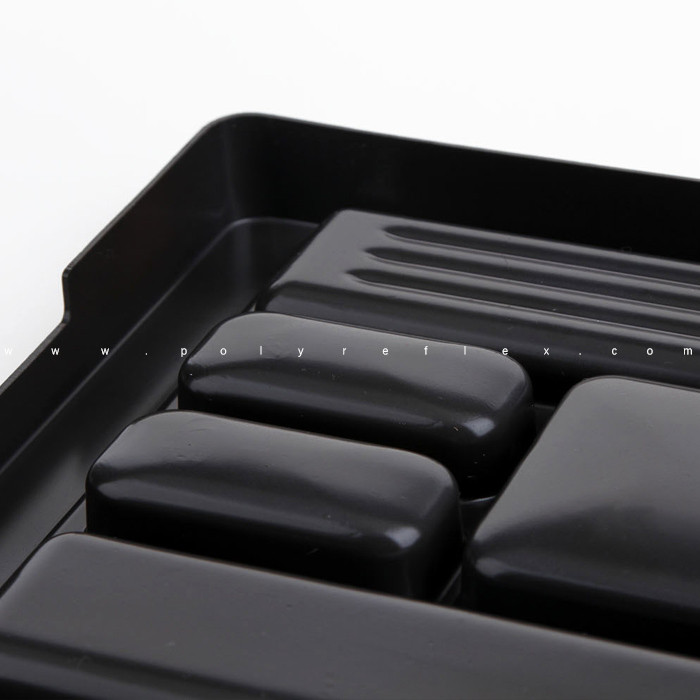
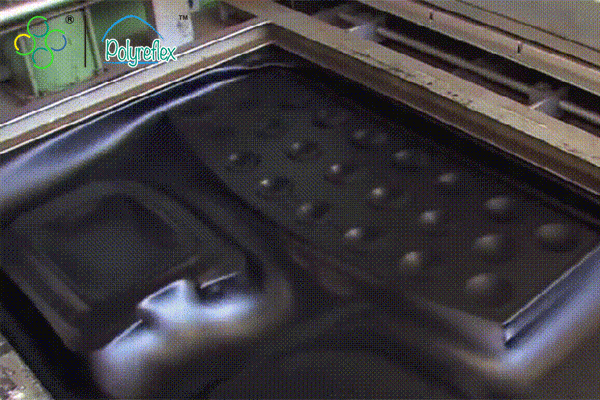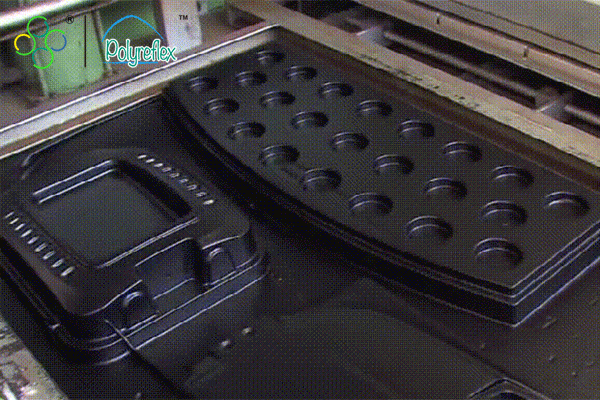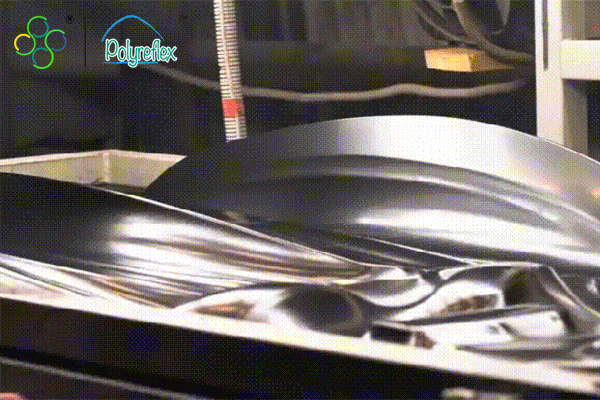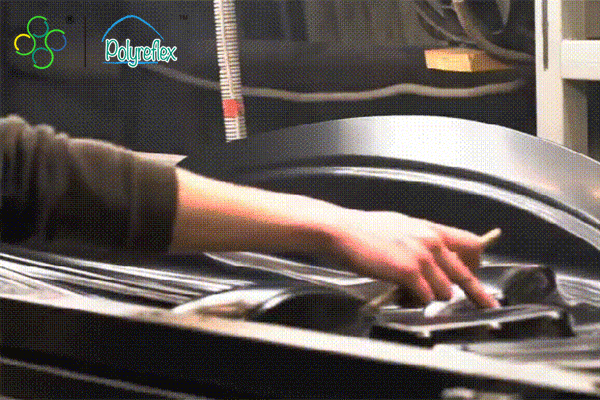
Vacuum forming is a widely used manufacturing process that involves shaping plastic sheets into various forms and products. It is a versatile technique suitable for producing both simple and complex shapes with relatively low tooling costs. The process begins with a flat sheet of thermoplastic material, such as ABS, PVC, or polycarbonate, being clamped into a frame. The sheet is then heated until it becomes pliable, either through heating elements or infrared heaters. Once the sheet reaches the desired temperature, it is stretched over a mold or form using vacuum pressure. A vacuum is applied underneath the sheet, causing it to conform to the shape of the mold. Once cooled, the formed part is removed from the mold, trimmed, and finished as needed.
The selection of the right material is crucial in vacuum forming, as it directly impacts the quality, durability, and functionality of the final product. Factors to consider when choosing a material include its heat resistance, impact strength, surface finish, and cost. Different materials offer varying levels of performance and suitability for specific applications. Understanding the properties and characteristics of each material is essential for achieving optimal results in vacuum forming. By selecting the right material, manufacturers can ensure the success of their vacuum forming projects and produce high-quality parts that meet the requirements of their customers.
Common Materials Used in Vacuum Forming
Vacuum forming encompasses a variety of thermoplastic materials, each offering unique properties suited for specific applications. Here's an overview of some common materials used in vacuum forming, along with a comparison of their key characteristics:
1. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is a widely used thermoplastic known for its excellent impact resistance, toughness, and affordability. It has good heat resistance, allowing it to maintain structural integrity during the vacuum forming process. ABS sheets are relatively easy to form and exhibit good surface finish, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They are commonly used in automotive parts, consumer goods, and electronic enclosures.
2. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is another popular thermoplastic used in vacuum forming due to its low cost and versatility. It offers good chemical resistance, weatherability, and flame retardancy, making it suitable for outdoor applications. However, PVC sheets have lower impact strength compared to ABS and may require additives for improved performance. PVC is commonly used in packaging, signage, and construction materials.
3. Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is a transparent thermoplastic known for its exceptional impact resistance and clarity. It has high heat resistance and can withstand elevated temperatures during the vacuum forming process. Polycarbonate sheets offer excellent dimensional stability and can be easily formed into complex shapes. They are commonly used in automotive lighting, aerospace components, and medical devices.
4. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
HDPE is valued for its high strength-to-density ratio, chemical resistance, and recyclability. While less commonly used in vacuum forming compared to ABS and PVC, HDPE sheets offer superior chemical resistance and durability. They are suitable for applications requiring resistance to acids, bases, and solvents. HDPE sheets are commonly used in industrial applications, such as containers, tanks, and trays.
5. PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
PETG is a transparent thermoplastic known for its excellent clarity, impact resistance, and ease of processing. It offers good chemical resistance and can be easily thermoformed into intricate shapes. PETG sheets are commonly used in retail displays, medical packaging, and point-of-purchase signage.
6. HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene)
HIPS is a versatile thermoplastic known for its high impact strength and dimensional stability. It offers good stiffness and can be easily formed into complex shapes. HIPS sheets are commonly used in packaging, automotive components, and consumer electronics.
When selecting a material for vacuum forming, it's essential to consider factors such as heat resistance, impact strength, surface finish, and cost. Each material has its advantages and limitations, and choosing the right material is crucial for achieving desired results in vacuum forming applications.
Advantages of ABS Sheets in Vacuum Forming
Introduction to ABS Sheets and their Properties:
ABS is a thermoplastic polymer known for its exceptional impact resistance, toughness, and versatility. It is composed of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, which impart unique properties to the material. ABS sheets are available in a variety of grades, offering different levels of impact strength, heat resistance, and surface finish. They can be easily thermoformed into complex shapes without losing their structural integrity, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
There are several reasons why ABS is well-suited for vacuum forming:
Excellent Impact Resistance: ABS sheets exhibit excellent impact resistance, making them capable of withstanding high-stress conditions during the vacuum forming process. This ensures that formed parts maintain their structural integrity and dimensional stability.Good Heat Resistance: ABS has good heat resistance, allowing it to maintain its shape and properties at elevated temperatures. This is essential for vacuum forming, where the material needs to be heated to a pliable state without degrading or warping.
Ease of Processing: ABS sheets are relatively easy to process and form into complex shapes using vacuum forming techniques. They can be heated quickly and uniformly, ensuring consistent forming and high-quality finished products.
Versatility: ABS is a versatile material that can be easily modified to meet specific application requirements. It can be colored, painted, or textured to achieve desired aesthetics and surface finishes. Additionally, ABS sheets can be combined with other materials or additives to enhance performance or functionality.
Vacuum formed products find widespread applications across various industries due to their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to produce complex shapes with relative ease. Here's a detailed overview of the diverse industries that utilize vacuum formed products and specific examples of products made through vacuum forming:
Diverse Industries that Utilize Vacuum Formed Products:
1. Automotive Industry: Vacuum formed products are extensively used in the automotive industry for interior and exterior components. These include dashboard panels, door trims, instrument clusters, wheel arch liners, and interior trim parts. Vacuum forming allows manufacturers to produce lightweight and durable automotive components with precise details and customized designs.
2. Electronics and Consumer Goods: Vacuum formed products are commonly found in the electronics and consumer goods sectors for housing and enclosures of various devices. Examples include computer housings, printer covers, TV and audio system enclosures, gaming console casings, and kitchen appliance components. Vacuum forming offers manufacturers the flexibility to produce aesthetically pleasing and functional enclosures that protect electronic components while maintaining a sleek and modern design.
3. Packaging Industry: Vacuum formed products play a crucial role in the packaging industry for creating custom packaging solutions. This includes blister packs, clamshell packaging, trays, and inserts for retail products. Vacuum forming allows for the creation of protective packaging that showcases products attractively while providing secure and tamper-resistant packaging solutions.
4. Medical and Healthcare: In the medical and healthcare sectors, vacuum formed products are used for various applications, including medical device housings, instrument trays, hospital bed components, and dental equipment. Vacuum formed products in this industry must meet stringent requirements for cleanliness, sterilization, and biocompatibility, making materials selection critical.
5. Point-of-Purchase (POP) Displays: POP displays are widely used in retail environments to showcase products and promote brand awareness. Vacuum formed products such as display stands, signage, and product dispensers are commonly used to attract customers' attention and enhance product visibility on store shelves. Vacuum forming allows for the creation of eye-catching displays with intricate designs and vibrant colors.
Specific Examples of Products Made through Vacuum Forming:
1. Blister Packs: Blister packs are transparent plastic packaging used to display and protect small items such as pharmaceuticals, toys, and hardware components. They consist of a thermoformed plastic blister attached to a backing card or film, providing a clear view of the product while keeping it secure and tamper-resistant.
2. Trays and Inserts: Vacuum formed trays and inserts are used for organizing and protecting products during shipping and storage. They are commonly used in industries such as food and beverage, electronics, and medical devices to securely hold items in place and prevent damage during transportation.
3. Helmet Liners: Helmet liners made through vacuum forming provide cushioning and impact protection in sports helmets, motorcycle helmets, and industrial safety helmets. Vacuum formed helmet liners are lightweight, durable, and customizable to provide a comfortable fit for users while ensuring optimal safety and protection.
4. Cosmetic Packaging: Vacuum formed cosmetic packaging includes containers, compacts, and cases for makeup products such as eyeshadows, blushes, and foundations. These packaging solutions are designed to showcase the product attractively while providing protection and convenience for consumers.
5. Truck Bed Liners: Vacuum formed truck bed liners provide durable and impact-resistant protection for truck beds, preventing damage from heavy cargo, tools, and equipment. These liners are custom-molded to fit specific truck models and offer superior durability and longevity compared to traditional bed liners.
In summary, vacuum formed products are integral to a wide range of industries, providing customized solutions for packaging, protection, display, and product housing. From automotive components to medical devices and retail displays, vacuum forming offers manufacturers the versatility and flexibility to meet diverse application requirements while maintaining cost-effectiveness and efficiency.
Polyreflex stands ready to assist readers in selecting the ideal thermoplastic sheet solution for their applications. With our expertise and comprehensive product range, we ensure that customers find the perfect fit for their specific needs. Contact us today for personalized assistance and explore the possibilities with Polyreflex as your trusted partner in material solutions.
In conclusion, ABS sheets offer a plethora of advantages that make them an optimal choice for vacuum forming applications. Their exceptional impact resistance, heat resistance, ease of processing, and versatility set them apart as a preferred material for producing high-quality vacuum formed products. From automotive components to electronics enclosures and packaging solutions, ABS sheets deliver reliable performance and aesthetic appeal across diverse industries.
Considering the benefits provided by ABS sheets in vacuum forming, we encourage readers to explore the possibilities and consider incorporating ABS sheets into their vacuum forming projects. Whether you're a manufacturer seeking efficient production solutions or a designer aiming for innovative product designs, ABS sheets offer the reliability, durability, and flexibility needed to bring your ideas to life. With Polyreflex's commitment to delivering top-tier ABS sheets tailored to meet your specific requirements, you can trust in the quality and performance of our products for your vacuum forming needs. Unlock the potential of ABS sheets and elevate your vacuum forming processes to new heights of success and efficiency.